Orbital molecular diagram mo oxygen o3 dioxygen o2 electrons c2 radical b2 configuration electron orbitals draw diagrams bonding energy level
Table of Contents
Table of Contents
If you’re a chemistry student, you’ve probably come across mo diagrams before. For the uninitiated, an MO or molecular orbital diagram is a visual representation of the molecular orbitals formed when atoms combine to form a molecule. It’s a crucial tool for predicting the properties and reactivity of molecules, which is why understanding how to draw mo diagrams is a must for any chemist. In this post, we’ll be discussing how to draw mo diagrams, step-by-step.
One of the biggest challenges with drawing mo diagrams is knowing where to start. Some students are intimidated by the complexity of the diagrams and find it difficult to make sense of the different molecular orbitals. Others struggle with the mathematical concepts that underlie the diagrams. Regardless of your specific pain points, learning how to draw mo diagrams is an essential part of mastering chemistry.
First, let’s take a closer look at what mo diagrams are and why they matter. In essence, an MO diagram represents the electron configuration of a molecule, showing how the individual atomic orbitals combine to form molecular orbitals. This, in turn, determines the bonding properties and energy levels of the molecule. For instance, by analyzing the MO diagram of a molecule, we can predict its stability, reactivity, and electronic properties.
Now that we know why MO diagrams are important let’s dive into how to draw them. To draw an MO diagram, we need to follow a few steps. First, we need to identify the number of valence electrons in each atom of the molecule. Second, we need to determine the type of bond and the bonding and antibonding orbitals. Finally, we can use the Aufbau principle to fill the orbitals with the electrons.
In summary, to draw MO diagrams, you need to identify the valence electrons, determine the type of bond, and fill the orbitals with electrons. The following sections provide a more detailed explanation of these steps, along with practical tips and examples to help you understand how to draw MO diagrams.
Step-by-Step Guide to Drawing MO Diagrams
Understanding how to draw MO diagrams requires a bit of practice and patience, but it’s definitely worth the effort. Here’s a step-by-step guide to help you get started.
Step 1: Identify the Valence Electrons
The first step in drawing an MO diagram is to identify the valence electrons of each atom in the molecule. These are the electrons that are involved in chemical bonding and determine the structure and properties of the molecule. To identify the valence electrons, you can refer to the periodic table and count the electrons in the outermost shell of each atom.

Step 2: Determine the Bond Type and Molecular Orbitals
The next step is to determine the type of bond formed between the atoms and the molecular orbitals that are involved. There are three types of bonds: covalent, ionic, and metallic, but we’ll focus on covalent bonds, which are the most common. In a covalent bond, the valence electrons of each atom overlap to form a shared pair of electrons. This results in the formation of two types of molecular orbitals: bonding and antibonding orbitals.

Step 3: Fill the Orbitals with Electrons Using the Aufbau Principle
The final step is to fill the molecular orbitals with electrons using the Aufbau principle, which states that electrons occupy the lowest energy orbitals first. You should start by filling the bonding orbitals with electrons, followed by the antibonding orbitals. When filling the orbitals, remember that each orbital can accommodate a maximum of two electrons, and the electrons should spin in opposite directions (i.e., one should be spin-up, and the other should be spin-down).
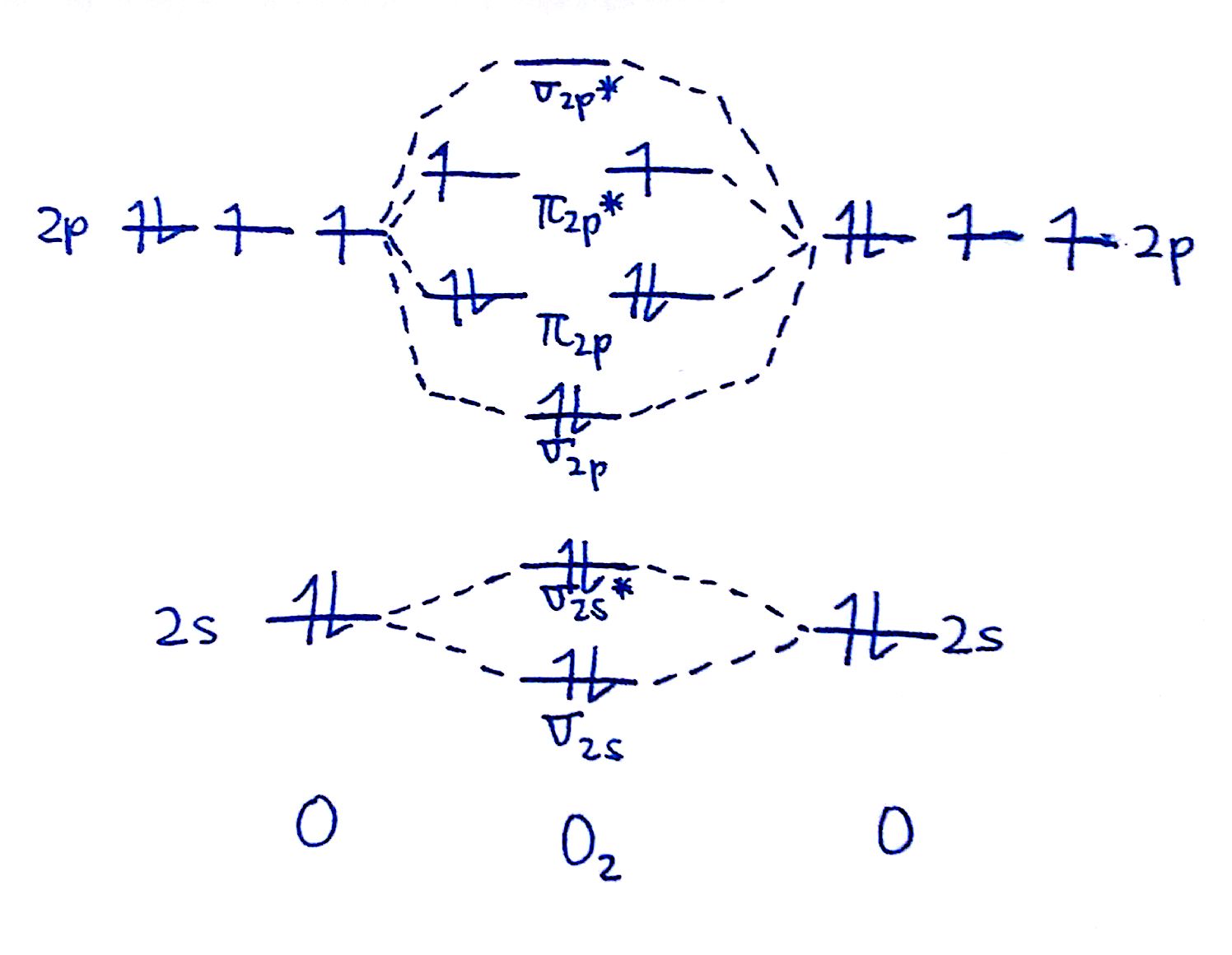
How to Draw MO Diagrams for More Complex Molecules
So far, we’ve looked at how to draw MO diagrams for simple diatomic molecules, but what about more complex molecules with multiple atoms? The process is similar, but the number of orbitals and electrons increases, making the diagrams more complex. Here are a few practical tips to help you draw MO diagrams for more complex molecules:
- Start by drawing the Lewis structure to determine the atom connectivity and the number of valence electrons in the molecule.
- Use the same steps outlined in the previous section but keep in mind that each atom has its own set of atomic orbitals that can interact with other atoms’ orbitals.
- Use symmetry to simplify the diagrams. Identify any symmetry elements in the molecule and use them to reduce the number of orbitals you need to analyze.

Common Mistakes When Drawing MO Diagrams
While it’s crucial to understand the steps involved in drawing MO diagrams, it’s equally important to avoid common mistakes that students make. Here are some of the most common mistakes to watch out for:
- Not identifying the valence electrons correctly: This can result in incorrect electron configurations and bonding properties.
- Confusing bonding and antibonding orbitals: Make sure you understand the difference between the two and how to fill them correctly with electrons.
- Overcomplicating the diagrams: Keep the diagrams simple and use symmetry to reduce the number of orbitals you need to analyze.
FAQ: How to Draw MO Diagrams
Here are some common questions students ask when learning how to draw MO diagrams, along with their answers:
Q: When do I need to draw MO diagrams?
A: You’ll need to draw MO diagrams if you want to predict the bonding properties and reactivity of a molecule. They’re also useful for understanding and predicting the electronic properties of molecules.
Q: What’s the difference between bonding and antibonding orbitals?
A: Bonding orbitals are formed when the atomic orbitals of different atoms overlap and create a shared pair of electrons, resulting in a stable bond. Antibonding orbitals are formed when atomic orbitals overlap out of phase, leading to the cancellation of the shared electron density and a destabilized bond.
Q: How do I determine the number of valence electrons in a molecule?
A: You can determine the number of valence electrons in a molecule by counting the electrons in the outermost shell of each atom. Alternatively, you can refer to the periodic table to determine the valence configuration of each element.
Q: What’s the importance of symmetry in MO diagrams?
A: Symmetry helps to simplify MO diagrams by reducing the number of orbitals you need to analyze. It also makes it easier to identify degenerate orbitals, which have the same energy level, and to predict the bonding properties of the molecule.
Conclusion of How to Draw MO Diagrams
Knowing how to draw MO diagrams is an essential skill for any chemistry student. While it may seem daunting at first, especially when dealing with complex molecules, with a bit of practice and patience, you can master this crucial tool. By following the steps outlined in this post, you can draw accurate and useful MO diagrams that will help you understand, predict, and explain the properties of molecules.
Gallery
MO Diagrams

Photo Credit by: bing.com / mo diagram diagrams draw orbital molecular
How To Draw Mo Diagram - Hanenhuusholli
Photo Credit by: bing.com / orbital
O3 Molecular Orbital Diagram

Photo Credit by: bing.com / orbital molecular diagram mo oxygen o3 dioxygen o2 electrons c2 radical b2 configuration electron orbitals draw diagrams bonding energy level
How To Draw Molecular Orbital Diagrams For Polyatomic Molecules

Photo Credit by: bing.com /
How To Draw Molecular Orbital Diagrams For Polyatomic Molecules

Photo Credit by: bing.com /






